The Bamboo Seed
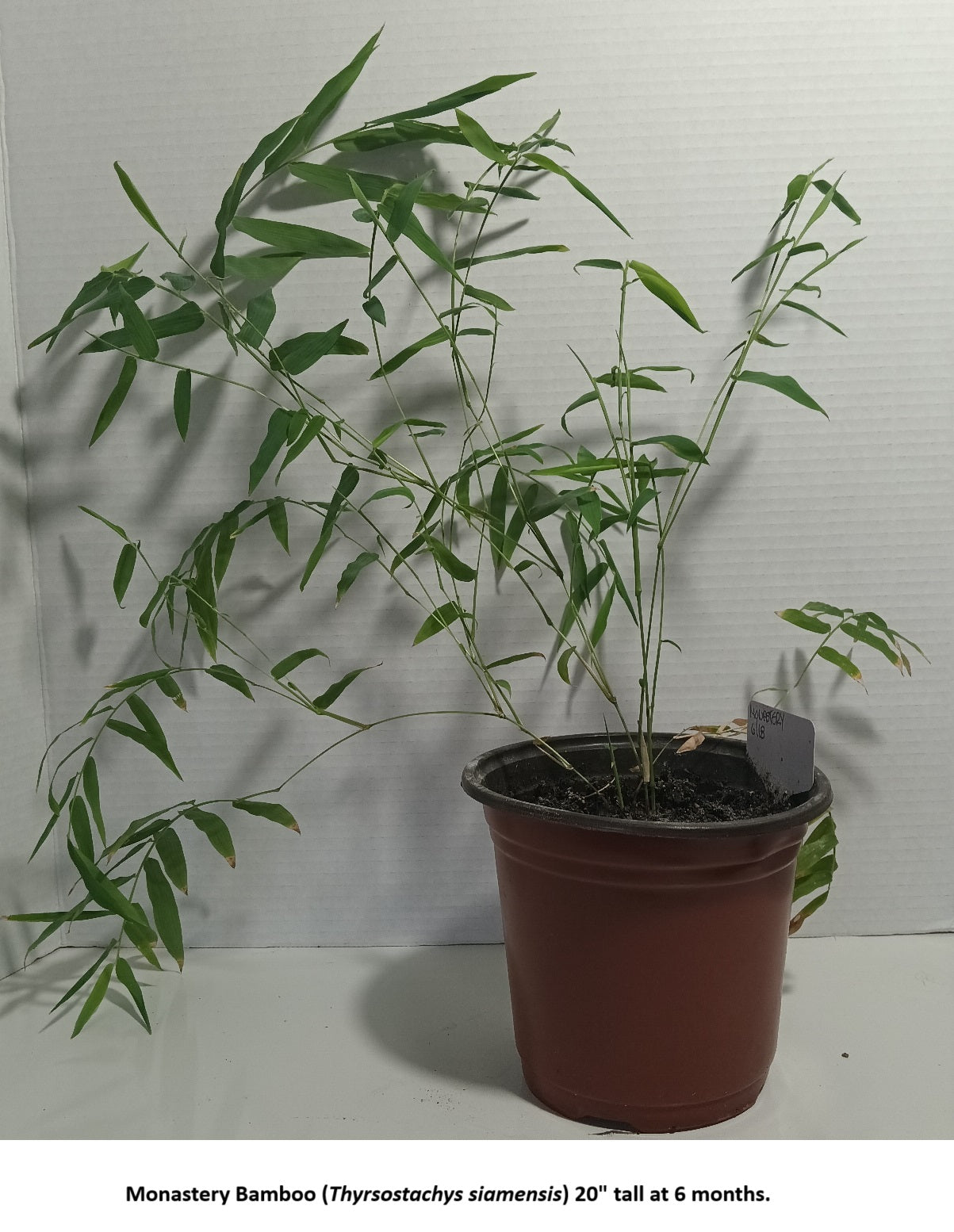
Monastery Bamboo Seeds - Thai Bamboo
Monastery Bamboo Seeds - Thai Bamboo
Couldn't load pickup availability
Monastery Bamboo Seeds for Sale
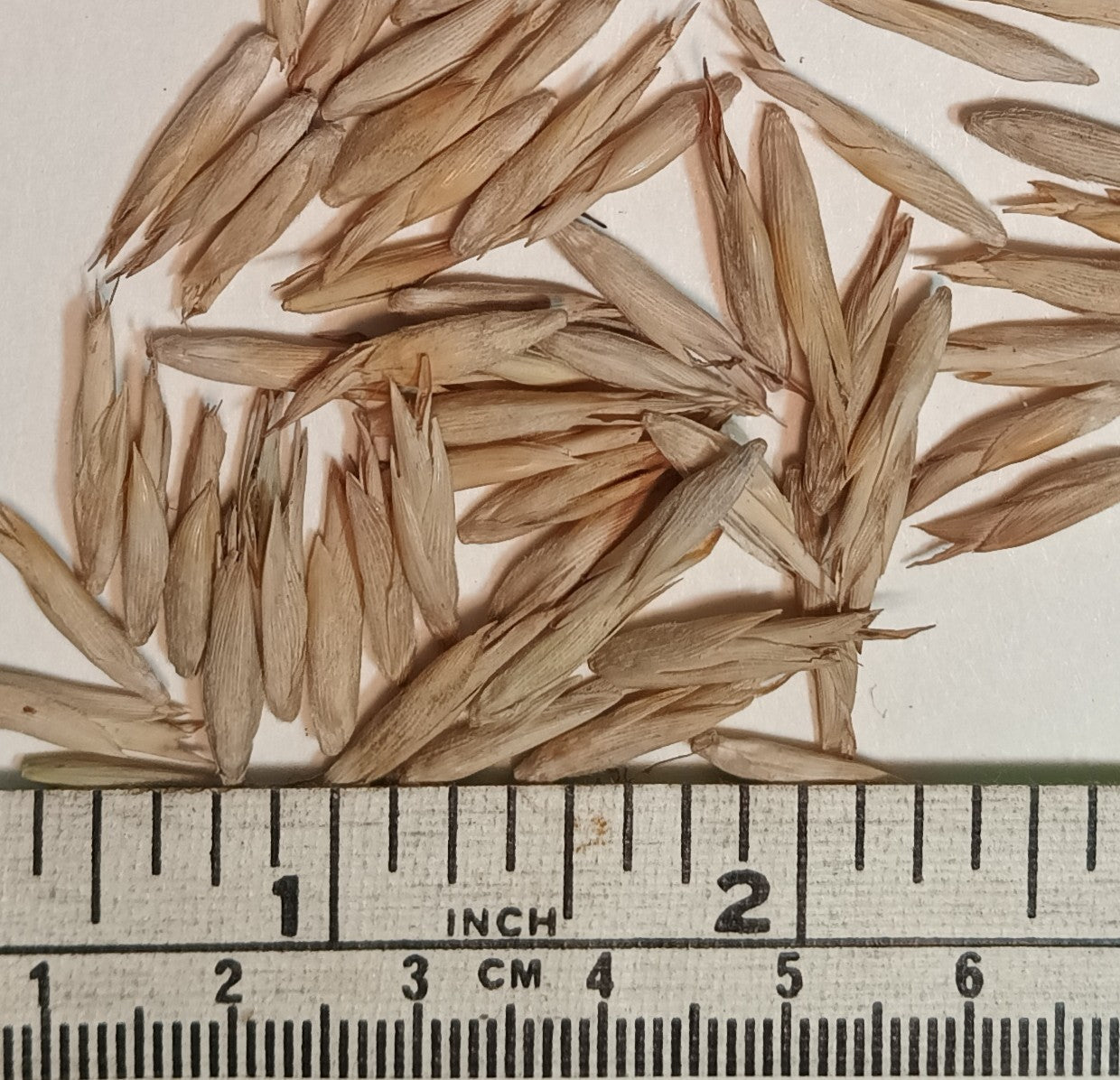
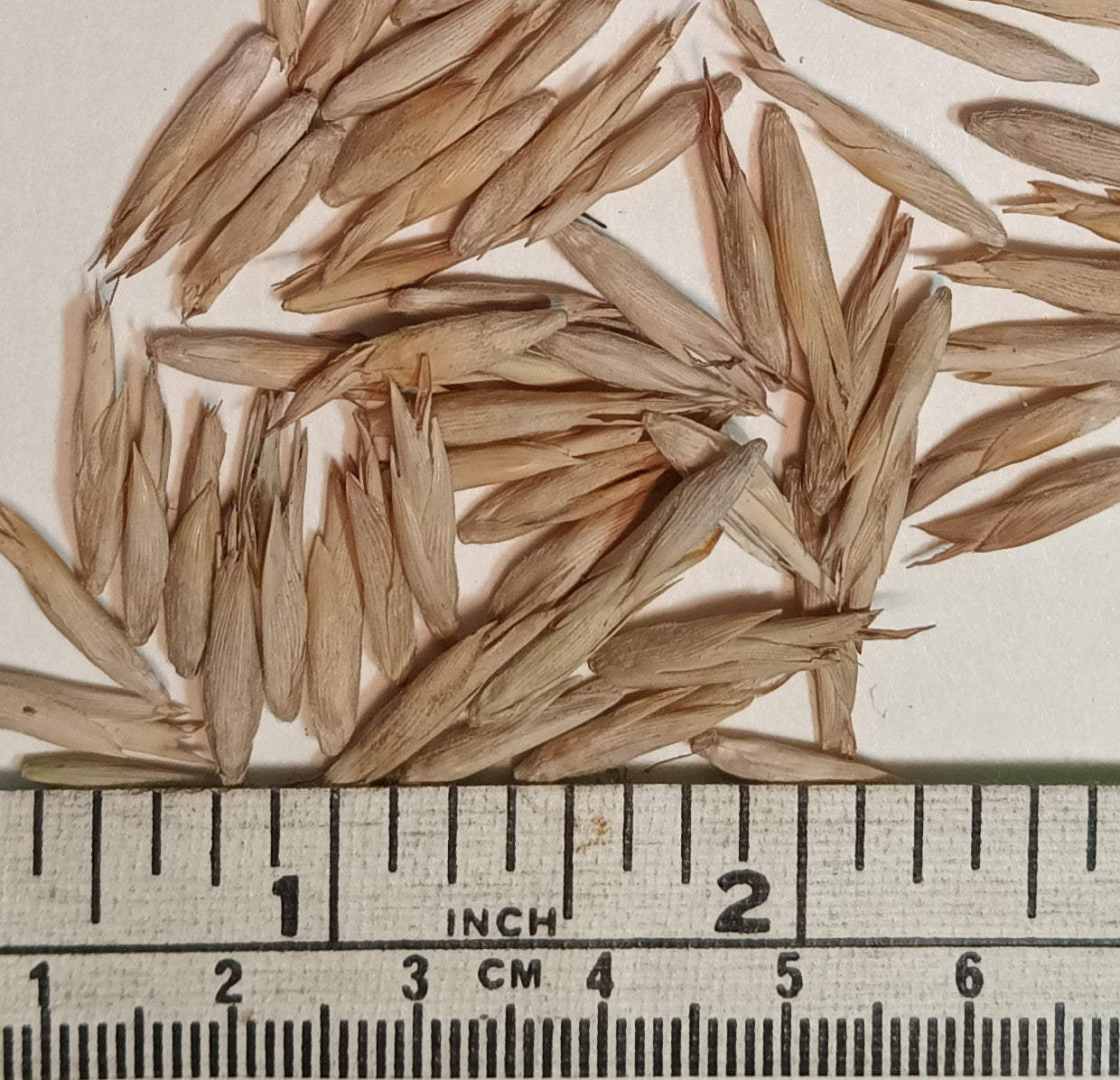
- Quantity 30+ Thai Monastery Bamboo seeds
- USDA Zones 9a-12; in zones 8a-8b when winterized
- Subtropical Temperate bamboo
- Cold Hardy to 20°F / -6.7°C
- Dense clumping bamboo seeds
- Non invasive bamboo seeds
- Height 50-65'
- Scientific name: Thyrsostachys siamensis
- Avg. days to first germination: 4-8
- When to Germinate: Any time
-
How to Germinate
Thyrsostachys siamensis Thai Monastery Bamboo Seeds
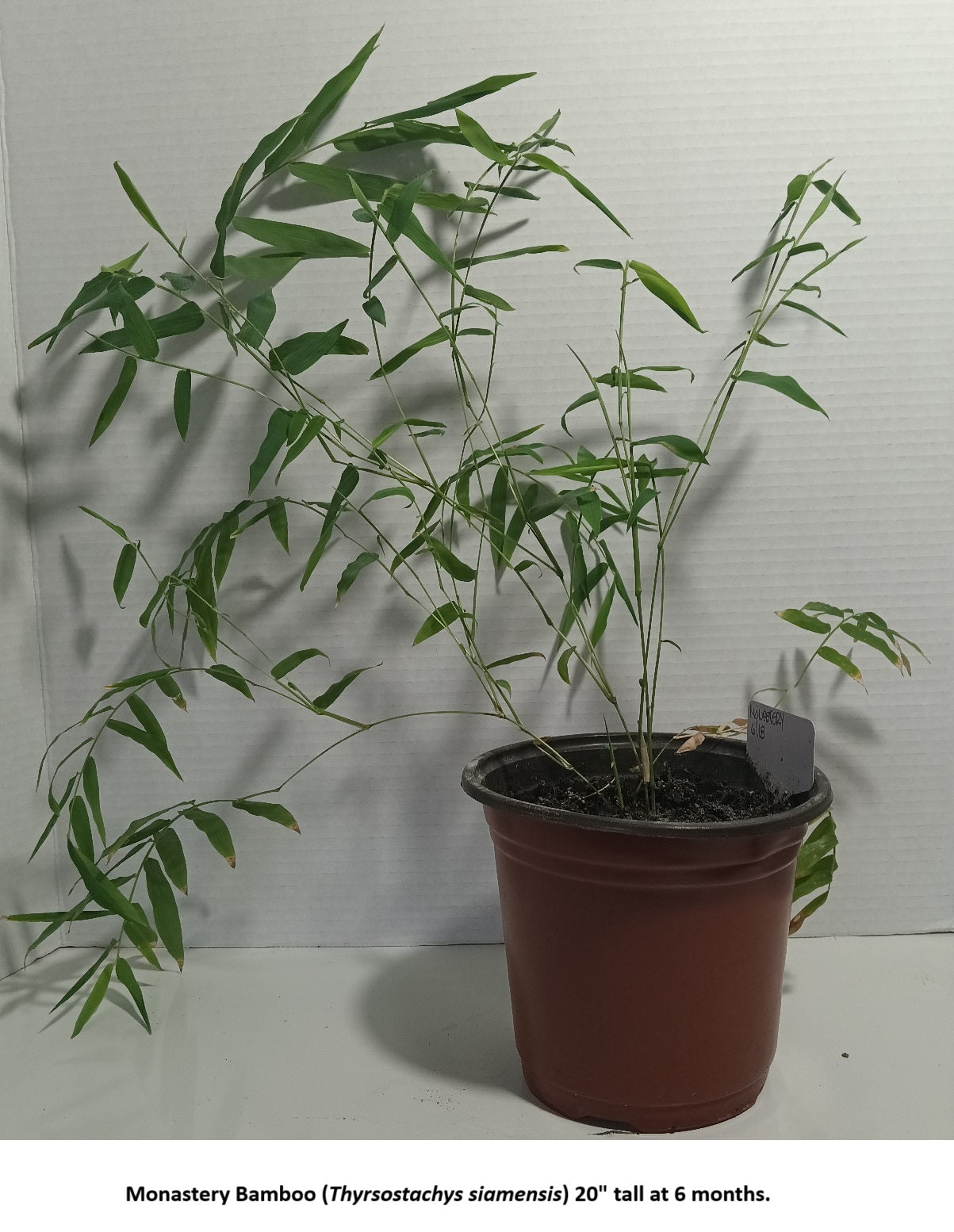
Thyrsostachys siamensis, commonly known as Monastery Bamboo, Thai Bamboo, Siam Bamboo, or Thai Temple Bamboo, is a species native to Southeast Asia, including Thailand. It is known for its graceful arching foliage, and is considered by many to be a visually outstanding ornamental bamboo for the garden landscape. With its gracefully hanging canopy and impressive height, Monastery Bamboo is an excellent choice for those seeking beautiful form with towering growth.
Some characteristics and traits of Monastery bamboo include:
Height: Thai Monastery bamboo is a relatively tall species, with mature culms (stems) reaching heights of up to 15-20 meters (50-65 feet). However, it tends to be shorter compared to some other bamboo species.
Culms: The culms of Thyrsostachys siamensis are typically slender and erect, with a diameter ranging from 4 to 8 centimeters (1.5 to 3 inches). They are characterized by distinctive, pronounced nodes along their length.
Color: When young, the culms of Siam bamboo often have a green coloration, which gradually transitions to a yellowish hue as they mature. The yellowish-brown color becomes more pronounced with age.
Leaves: The leaves of Thyrsostachys siamensis are long and narrow, typically measuring around 15-30 centimeters (6 to 12 inches) in length. They are arranged alternately along the culms and have a lanceolate shape.
Branching: Monastery bamboo tends to have more distributed foliage compared to some other bamboo species. The branches form at irregular intervals along the culms, contributing to its open and airy appearance.
Rhizomes: A clumping, non-invasive bamboo species, Thyrsostachys siamensis spreads via underground rhizomes, enabling it to propagate vegetatively over time.
Habitat: Thai Monastery bamboo is well-suited to tropical and subtropical climates, naturally thriving in regions with warm temperatures and high humidity with cold hardiness to 20F/-4C. It prefers moist, well-drained soils and is commonly found growing in forests, gardens, and along riverbanks throughout Southeast Asia.
Utilization: Thyrsostachys siamensis Thai bamboo is valued for its versatility and has various practical and cultural uses. Its slender culms make it suitable for construction purposes, including building materials for traditional houses, fences, and handicrafts. Additionally, it is utilized for making furniture, baskets, and musical instruments. In some cultures, Siam bamboo shoots are also consumed as a delicacy.
|
|
|
About Seeds for Thyrostachys Bamboo
The Thyrsostachys genus is a group of bamboo species native to Southeast Asia, particularly Thailand and neighboring regions. Here's an overview of the natural history of the Thyrsostachys genus:
Taxonomy: The Thyrsostachys genus belongs to the grass family Poaceae, subfamily Bambusoideae. It includes several species, with Thyrsostachys siamensis being one of the most well-known and commonly cultivated members of the genus.
Distribution: Species within the Thyrsostachys genus are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions of Southeast Asia, including Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, and southern China. They typically inhabit diverse habitats such as forests, riverbanks, and hillsides.
Habitat: Thyrsostachys bamboo species thrive in warm, humid climates with well-drained soils. They are often found growing alongside rivers, streams, and in lowland forests. Some species may also tolerate a range of altitudes, from lowland areas to montane regions.
Morphology: Bamboo species in the Thyrsostachys genus share several morphological characteristics. They typically have slender culms (stems) with distinctive nodes and internodes. The leaves are long and narrow, arranged alternately along the culms. Inflorescences, when present, are typically in the form of compact spikes or panicles.
Reproduction: Thyrsostachys bamboo species reproduce both sexually, via flowering and seed production, and vegetatively, through underground rhizomes. Flowering in bamboo is an infrequent event, occurring at intervals ranging from several years to several decades, depending on the species. After flowering, the bamboo typically dies, but new shoots emerge from the rhizomes to replenish the population.
Ecological Importance: Bamboo species in the Thyrsostachys genus play a vital role in their ecosystems. They provide habitat and food for various wildlife species, including birds, mammals, and insects. Bamboo forests also help stabilize soils, prevent erosion, and regulate water flow in river systems.
Cultural Significance: Throughout history, Thyrsostachys bamboo species have been deeply intertwined with the cultures and traditions of Southeast Asia. They are used for a wide range of purposes, including construction materials, handicrafts, furniture, musical instruments, and culinary uses. Bamboo has symbolic significance in many cultures, representing resilience, strength, and adaptability.
Conservation: While some Thyrsostachys bamboo species are widespread and abundant, others may face threats due to habitat loss, deforestation, and overexploitation. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these valuable resources and maintain biodiversity in bamboo ecosystems.
Growing Monastery Bamboo from Seed
Planting Monastery Bamboo (Thyrsostachys siamensis) in your landscape offers numerous benefits, both aesthetic and functional. This elegant clumping bamboo is known for its upright, tightly packed growth habit, making it ideal for creating natural privacy screens or ornamental focal points. Its lush green foliage and straight, golden culms add a tropical, serene ambiance to gardens, patios, or along property lines. Unlike running bamboos, Monastery Bamboo is non-invasive, easy to maintain, and suitable for smaller spaces. It thrives in warm climates, tolerates pruning well, and provides year-round greenery, enhancing the overall beauty and tranquility of any outdoor space.
Thyrsostachys genus of bamboo is an important component of the natural and cultural heritage of Southeast Asia, contributing to the region's biodiversity, ecosystem services, and cultural traditions.
Find similar clumping bamboo seeds currently in stock.










Collections
-

All Bamboo Seeds for Sale
Welcome to our catalog of bamboo plant seeds for sale including clumping...
-

All Flower Seeds
All of our 2025 flower seeds are sold out. Please check back...
-

All Ornamental Grass Seeds
Grass has finally come into its own as a garden landscape centerpiece....
-
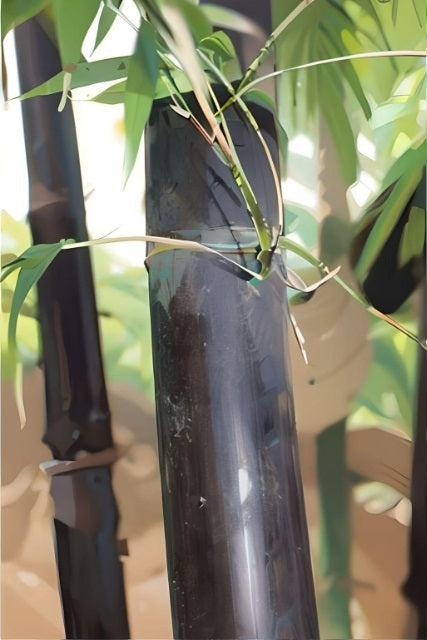

Black Bamboo Seeds
Consider Black Bamboo seeds for eye-catching bamboo varieties with lustrous black, dark...
-
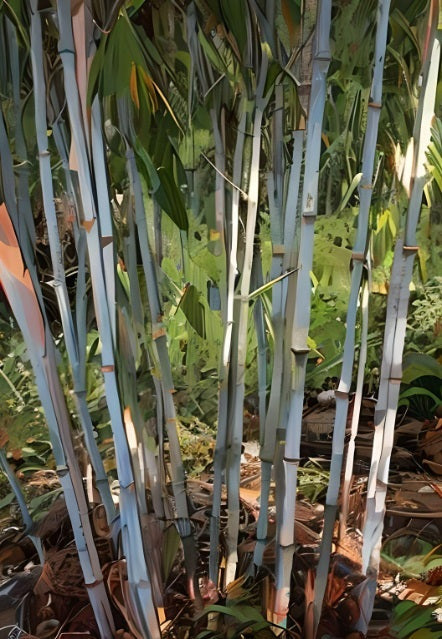

Clumping Bamboo Seeds
Clumping bamboo species grow in dense clumps or clusters that are naturally...
-

Cold Hardy Bamboo Seeds
A selection of cold resistant bamboo seeds for hardy bamboo able to...
-

Fargesia Bamboo Seeds - Clumping and Cold Hardy
Buy bamboo seeds for beautiful cold hardy and clumping Fargesia bamboo. Our...
-

Giant Bamboo Seeds
When you're looking for impressive size with ample shade below, consider fastest...
-

Running Bamboo Seeds
Running bamboo spreads through underground runners, known as rhizomes. These rhizomes can...
-

Tropical Bamboo Seeds
Our curated selection of tropical bamboo seeds best suited for planting in...