The Bamboo Seed
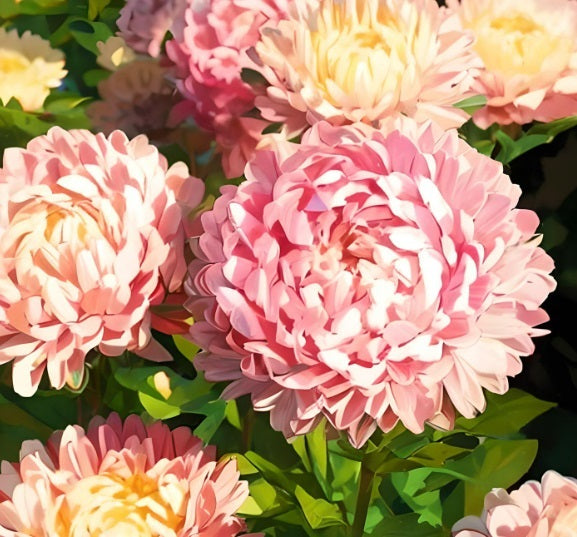
Aster Seeds - Callistephus Tall Paeony Duchess Pink
Aster Seeds - Callistephus Tall Paeony Duchess Pink
Couldn't load pickup availability
Pink Aster Seeds for Sale
- Quantity 100+ Aster seeds
- Botanical name: Callistephus Tall
- USDA zone 3-9
- Height: Up to 28"
- Full sun, blooms Summer, Fall
- Annual flower seeds
Pink Peony Aster Seeds
Aster flowers, also known as Michaelmas daisies or starworts, are popular garden flowers that belong to the Asteraceae family. They are native to North America, Europe, and Asia and are known for their vibrant colors and daisy-like appearance. Here are some key characteristics of aster flowers:
Peony Duchess Aster Seeds
Appearance: Aster flowers have a daisy-like appearance with a central disk surrounded by numerous ray-like petals. The disk can be yellow, while the ray petals come in various colors such as white, pink, purple, blue, or lavender. The petals often have a slender and elongated shape, giving the flower a star-like appearance.
Flowering Season: Asters typically bloom in late summer or fall, adding a splash of color to the garden when many other flowers are starting to fade. The exact flowering season can vary depending on the species and cultivar.
Size: Aster flowers can vary in size, depending on the species and variety. They range from small, delicate flowers to larger, showy blooms. The height of the plants can also vary, with some asters growing to just a few inches tall and others reaching up to several feet in height.
Color Variations: Asters come in a wide range of colors, providing various options for gardeners. Common colors include white, pink, purple, blue, and lavender. Some asters even have bi-colored petals, featuring combinations like white and pink or purple and white.
Longevity: Asters are generally long-lived perennials, meaning they come back year after year. With proper care and growing conditions, they can continue to bloom and thrive for several seasons.
Attracts Pollinators: Asters are known for attracting pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects. The nectar-rich flowers serve as a valuable food source for these creatures, making asters a great addition to pollinator-friendly gardens.
Sun and Soil Requirements: Most asters prefer full sun to partial shade for optimal growth and flowering. They typically thrive in well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. Asters can tolerate a range of soil types but prefer soil that is slightly acidic to neutral pH.
Low Maintenance: Asters are generally easy to grow and require minimal maintenance. They are relatively drought-tolerant once established but benefit from regular watering during dry spells. Deadheading spent flowers can encourage more blooms and extend the flowering season.
Companion Plants: Asters can be combined with other garden plants to create attractive and harmonious displays. They work well with ornamental grasses, coneflowers, goldenrods, sedums, and fall-blooming perennials.
Symbolism: Asters are often associated with positive meanings, including love, patience, and daintiness. They are sometimes considered as symbols of elegance, charm, and enchantment.
These are some of the notable characteristics of aster flowers. With their beautiful blooms and ability to attract pollinators, asters are a popular choice for gardens, especially during the late summer and fall seasons.
Growing asters from seeds is a rewarding process that can be accomplished by following these steps:
Timing: Start the seed germination process indoors about 6 to 8 weeks before the last frost date in your area. This will ensure that the seedlings are ready to be transplanted outdoors when the weather is suitable.
Seed selection: Choose high-quality aster seeds from a reputable source or save seeds from mature aster plants in your garden. Look for a variety that suits your preferences in terms of color, height, and flower shape.
Seed starting containers: Use seed trays or small pots with drainage holes to start your aster seeds. Fill the containers with a seed starting mix, which provides a light and well-draining medium for the seeds.
Sowing seeds: Sow the aster seeds on the surface of the seed starting mix. Gently press them into the soil, but avoid burying them too deeply, as aster seeds require light to germinate. Space the seeds about an inch apart to provide enough room for growth.
Watering: After sowing the seeds, water the containers gently using a misting spray bottle or a watering can with a fine rose attachment. Keep the soil consistently moist but not overly saturated. Avoid allowing the soil to dry out completely.
Germination: Place the seed trays in a warm and well-lit location, preferably near a south-facing window or under grow lights. Aster seeds usually take around 1 to 2 weeks to germinate. Once the seedlings emerge, provide them with sufficient light to prevent them from becoming leggy.
Transplanting: When the seedlings have developed their second set of true leaves, they are ready to be transplanted into individual pots or into the garden. Carefully separate the seedlings and transplant them into larger containers or directly into well-prepared garden soil.
Harden off: Before transplanting the seedlings outdoors, gradually acclimate them to outdoor conditions. Over the course of about a week, expose the seedlings to increasing amounts of sunlight and outdoor temperatures. Start with a few hours of exposure and gradually increase the duration each day.
Planting outdoors: Choose a sunny location in your garden with well-drained soil. Space the aster plants according to the specific variety you are growing, usually about 12 to 18 inches apart. Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball of the seedling, place it in the hole, and gently firm the soil around it.
Maintenance: Water the newly transplanted seedlings thoroughly and continue to keep the soil evenly moist during the establishment period. Once established, asters generally require about 1 inch of water per week. Apply a layer of organic mulch around the plants to help conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
Support and care: As the aster plants grow, they may require support to prevent them from flopping over. Install stakes or use plant supports early in the season to provide necessary support. Additionally, pinch back the plants when they reach about 6 inches in height to encourage bushier growth and more abundant blooms.
Blooming: Depending on the aster variety, flowering typically occurs in late summer or early fall. Enjoy the beautiful display of colorful blooms, and consider deadheading (removing spent flowers) to encourage continuous blooming.
Growing Peony Aster Flowers from Seed
By following these steps, you can successfully grow asters from seeds and enjoy their vibrant flowers in your garden. Remember to consult specific instructions for the aster variety you are growing, as certain types may have unique requirements.

Collections
-

All Bamboo Seeds for Sale
Welcome to our catalog of bamboo plant seeds for sale including clumping...
-

All Flower Seeds
All of our 2025 flower seeds are sold out. Please check back...
-

All Ornamental Grass Seeds
Grass has finally come into its own as a garden landscape centerpiece....
-

Black Bamboo Seeds
Consider Black Bamboo seeds for eye-catching bamboo varieties with lustrous black, dark...
-

Clumping Bamboo Seeds
Clumping bamboo species grow in dense clumps or clusters that are naturally...
-

Cold Hardy Bamboo Seeds
A selection of cold resistant bamboo seeds for hardy bamboo able to...
-
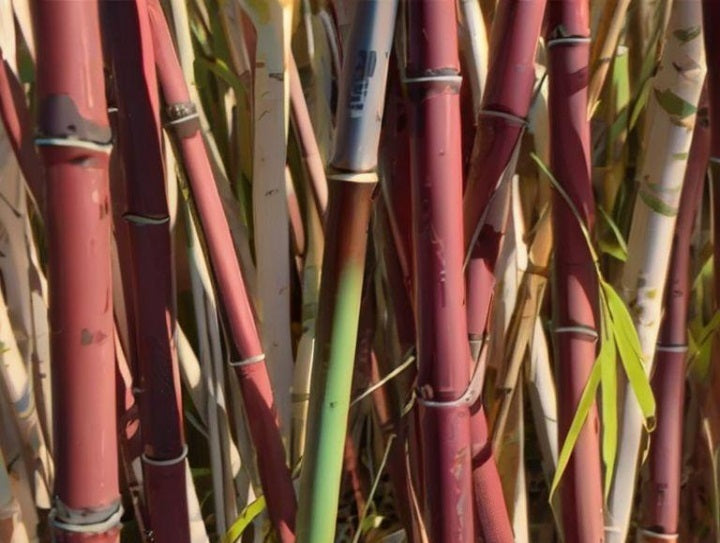

Fargesia Bamboo Seeds - Clumping and Cold Hardy
Buy bamboo seeds for beautiful cold hardy and clumping Fargesia bamboo. Our...
-
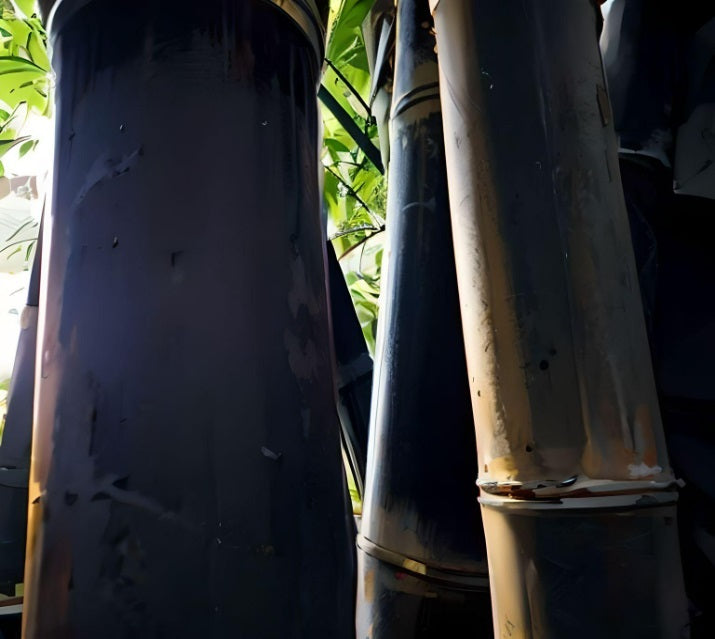

Giant Bamboo Seeds
When you're looking for impressive size with ample shade below, consider fastest...
-
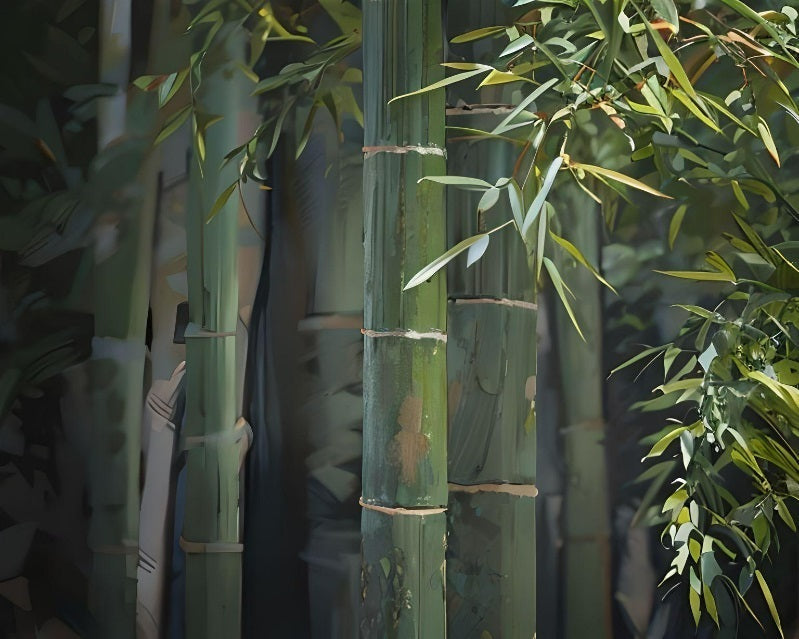

Running Bamboo Seeds
Running bamboo spreads through underground runners, known as rhizomes. These rhizomes can...
-
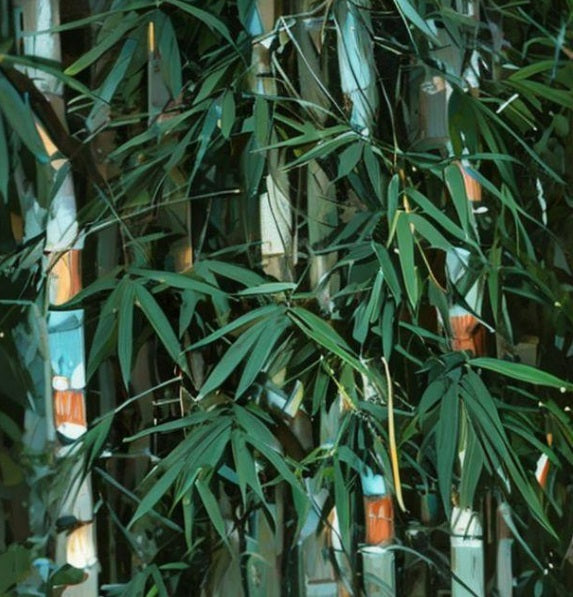

Tropical Bamboo Seeds
Our curated selection of tropical bamboo seeds best suited for planting in...